Order fulfilment errors cost Australian e-commerce businesses millions annually in returns processing, replacement shipments, and lost customer loyalty. As consumer expectations for rapid delivery intensify, manual order picking operations face mounting pressure from labour shortages, human error, and processing bottlenecks that compromise delivery timelines.
Automated order picking offers a strategic response to these operational challenges. Modern warehouses across Australia are adopting these technologies to achieve measurable improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. This article examines what automated order picking involves, the core technologies powering these systems, the business benefits they deliver, and their applications across key industries.
What Is Automated Order Picking?
Automated order picking uses technology and machinery to retrieve products from warehouse storage locations with minimal human intervention. The primary objective is accelerating the journey from shelf to packing station, ready for dispatch.
Traditional manual picking requires workers to walk kilometres daily through warehouse aisles, physically locating and retrieving items. This approach introduces fatigue-related errors, creates physical strain, and limits throughput capacity. SmartlogitecX automated systems eliminate these constraints by bringing goods to stationary pickers or handling the entire retrieval process robotically.
Think of it as transforming your warehouse from a manual library into a high-speed, self-organising distribution centre. SmartlogitecX helps Australian businesses understand these solutions and identify implementation pathways suited to their operational requirements.
Core Technologies Driving Automated Picking Systems
Automated picking represents an ecosystem of integrated solutions rather than a single technology. Understanding each component helps businesses evaluate which combinations suit their specific needs.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
SmartlogitecX AS/RS consists of high-density storage structures with automated cranes or shuttles that retrieve and store goods. These systems maximise vertical warehouse space, allowing facilities to hold significantly more inventory within the same footprint. AS/RS excels in high-volume environments where speed and density matter.
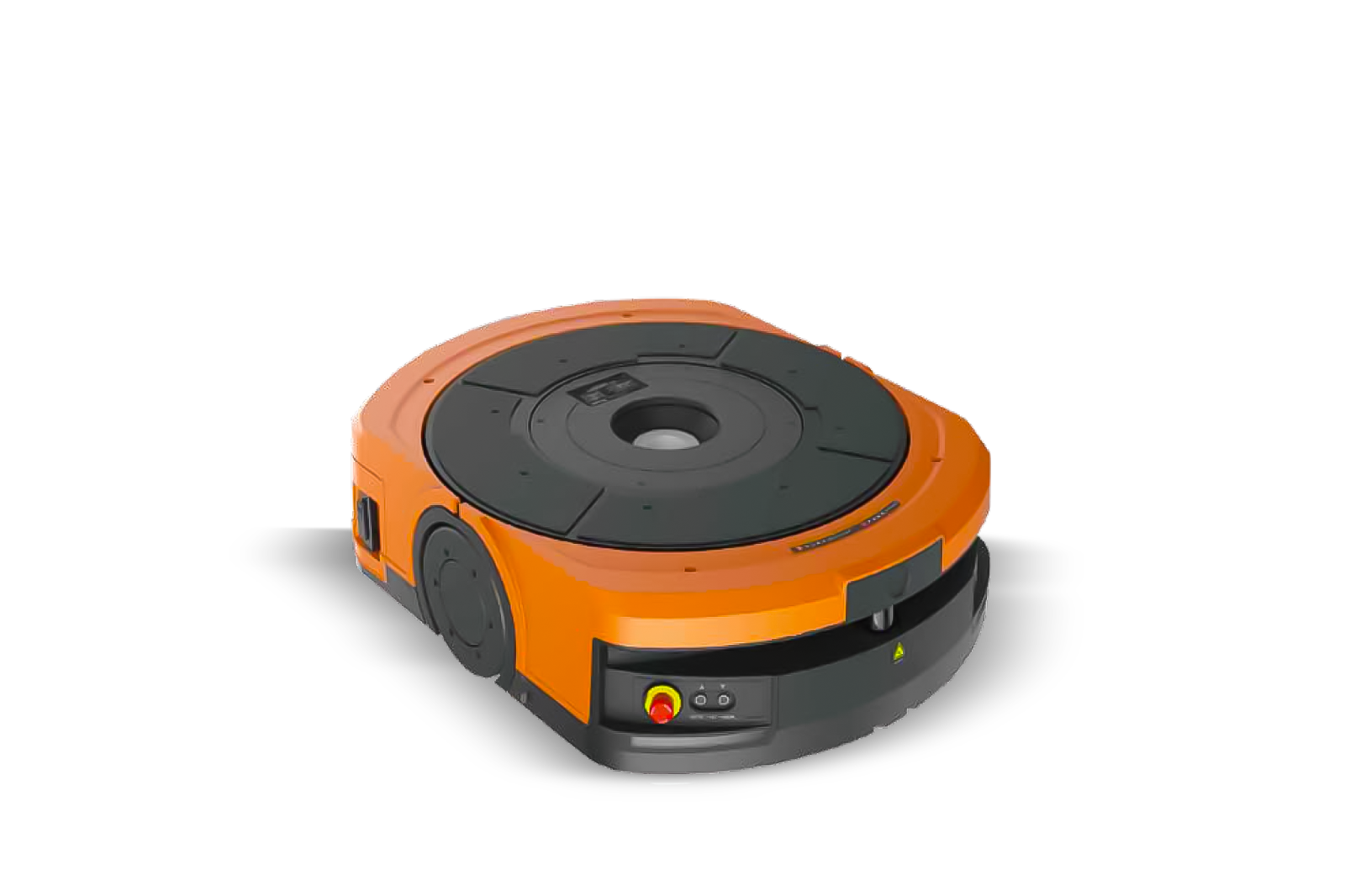
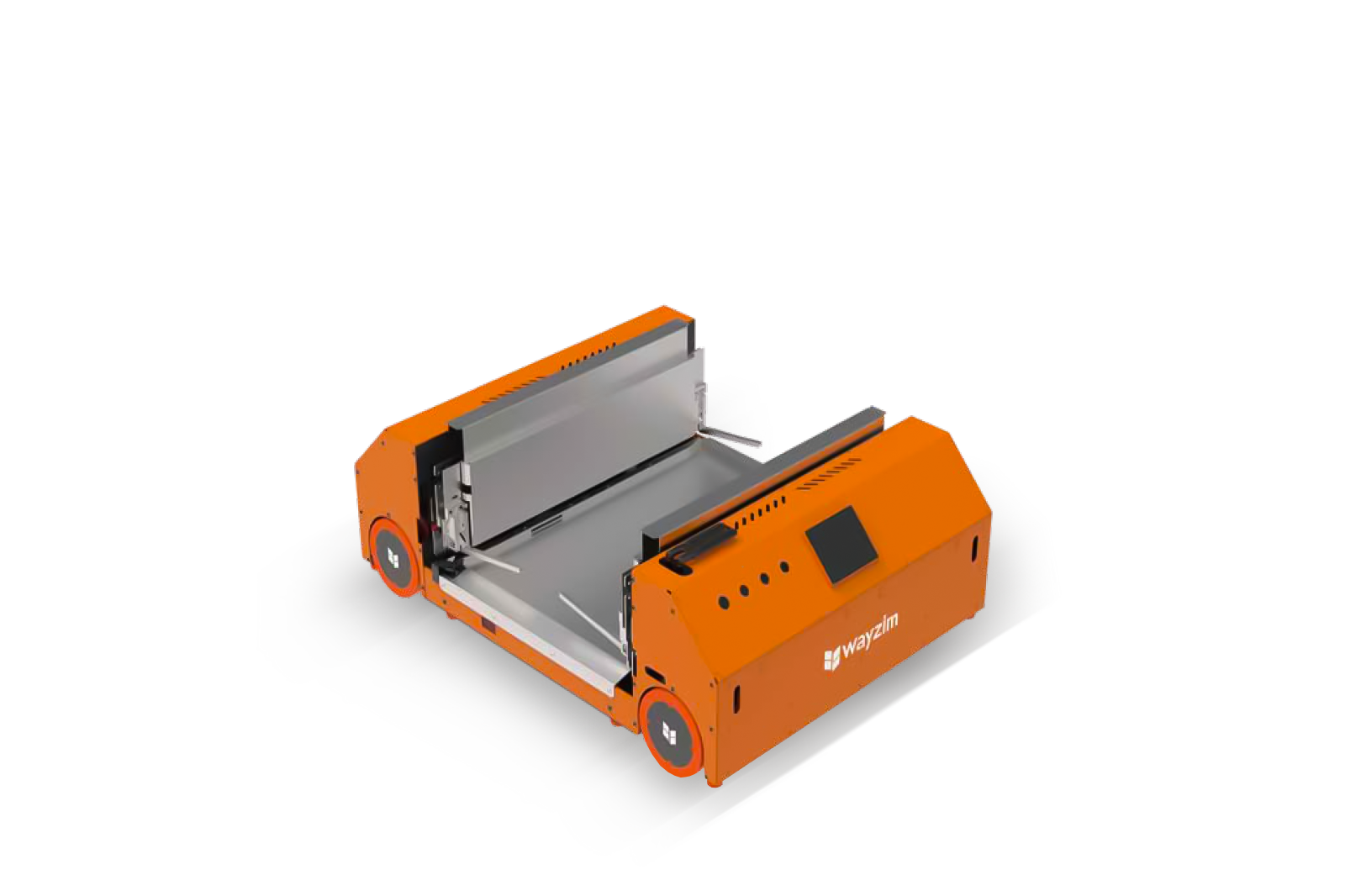
Autonomous Mobile Robots and AGVs
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) transport goods between storage locations and pick stations. The key difference lies in navigation: AGVs follow fixed paths using magnetic tape or wires embedded in flooring, whilst AMRs use sensors and artificial intelligence to navigate dynamically around obstacles.
AMRs offer greater flexibility for facilities with changing layouts or high traffic variability. Both function as automated warehouse robots that reduce manual transport time significantly.
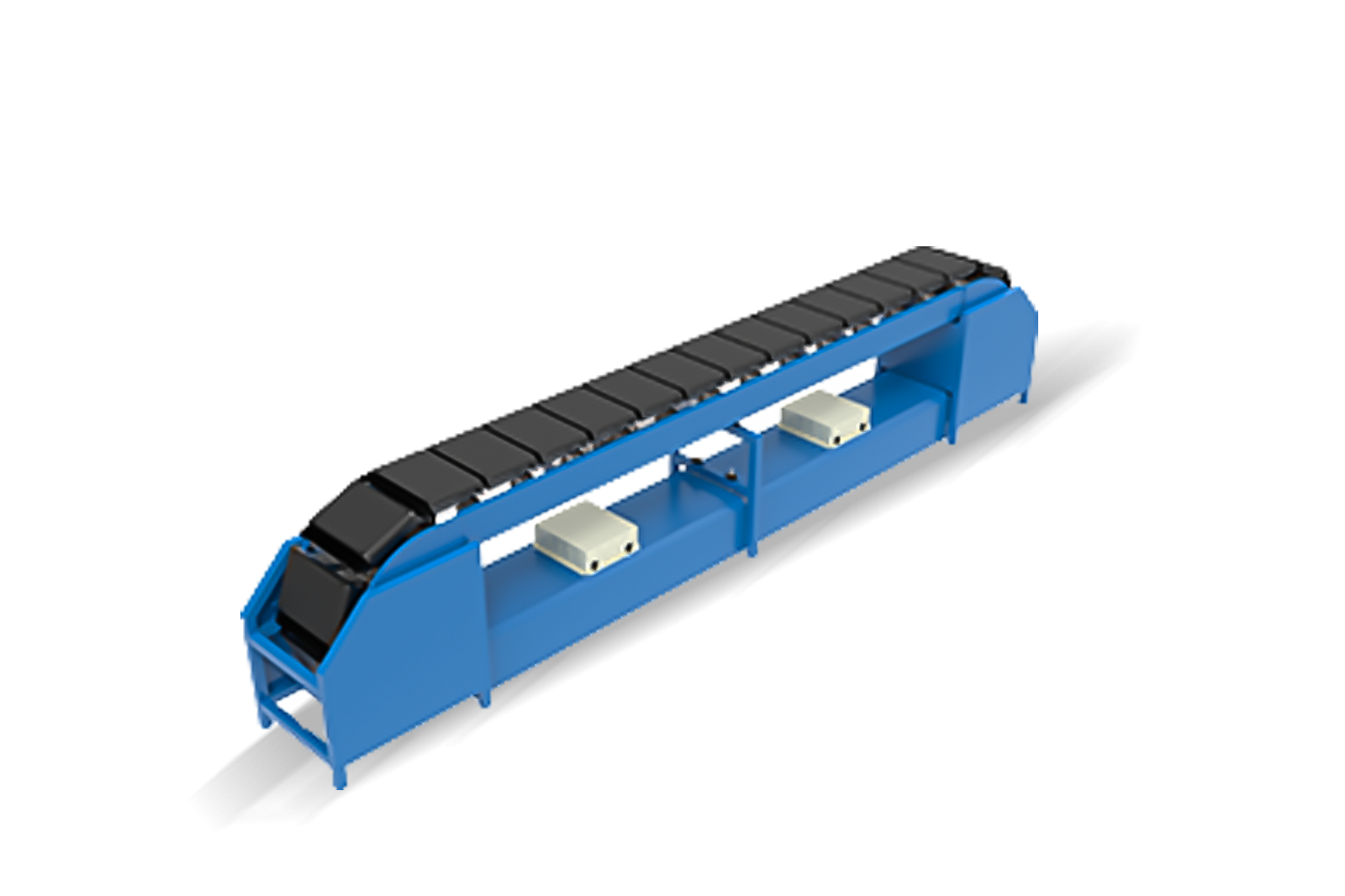
Robotic Picking and Sortation Solutions
Robotic arms equipped with vision systems and AI handle piece picking—selecting individual items from bins or shelves. These systems identify products by shape, size, and barcode, then use specialised grippers to place items into order totes. Automated sortation systems then direct picked items to appropriate packing stations based on destination or order priority.
Pick-to-Light and Voice Picking Systems
These technologies augment human pickers rather than replacing them entirely. Pick-to-light systems use LED displays to guide workers to correct items and quantities. Voice picking provides verbal instructions through headsets, enabling hands-free operation. Both reduce training time and improve accuracy for manual picking operations.
The Warehouse Management System as Central Hub
The warehouse management system (WMS) functions as the operational brain, integrating all technologies into a cohesive workflow. WMS software optimises picking routes, manages real-time inventory levels, assigns tasks to both robots and human workers, and provides performance analytics.
SmartlogitecX assists businesses in evaluating which technology combinations align with their operational scale, product mix, and growth objectives.
Key Benefits of Warehouse Picking Automation
Decision-makers evaluating automation investments should understand the measurable business outcomes these systems deliver.
Achieving Superior Order Accuracy
Automated systems minimise mis-picks, wrong quantities, and incorrect shipments through barcode verification and vision-guided picking. Many facilities report accuracy rates exceeding 99.9%, reducing costly returns and improving customer satisfaction scores.
Increasing Speed and Operational Throughput
Automated picking systems operate continuously at consistent speeds without fatigue-related slowdowns. This capability significantly increases daily order processing capacity—critical during peak seasons when demand surges unpredictably.
Reducing Labour Costs and Dependency
Automation addresses persistent challenges including labour shortages, wage inflation, and high staff turnover in warehouse environments. Rather than eliminating jobs, these systems shift employees toward value-added tasks such as quality control, exception handling, and system oversight.
Optimising Warehouse Space Utilisation
AS/RS and similar solutions utilise vertical space that traditional shelving cannot access. Facilities often achieve 40-60% higher inventory density within existing footprints, delaying or eliminating the need for costly facility expansion.
Enhancing Worker Safety and Ergonomics
Automation reduces repetitive strain injuries, lifting accidents, and other physical risks associated with manual picking. Employees benefit from less physically demanding roles whilst facilities reduce workers’ compensation costs.
SmartlogitecX partners with Australian warehouses to quantify these benefits within their specific operational context.
Real-World Applications Across Key Industries
Automated order picking serves diverse sectors, each with distinct requirements.
E-Commerce and Retail Fulfilment
Online retailers rely on automation to meet same-day and next-day delivery expectations, particularly during peak periods like Black Friday and holiday seasons. The ability to scale throughput without proportional labour increases provides critical competitive advantage.
Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Operations
Pharmaceutical distribution demands precision, traceability, and error-free handling. Automated systems provide audit trails for regulatory compliance whilst eliminating potentially dangerous medication errors.
Food, Beverage, and Cold Storage Logistics
Automation manages inventory with expiration dates, handles delicate items appropriately, and operates in cold storage environments where extended manual labour presents health and safety challenges.
Third-Party Logistics Providers
3PL providers use automation to efficiently manage inventory and fulfilment for multiple clients with diverse product types, improving service levels and profitability across their customer base.
Final Thoughts on Boosting Order Fulfilment
Automated order picking has evolved from futuristic concept to practical necessity for businesses pursuing growth and customer loyalty. The benefits—enhanced accuracy, greater speed, improved operational efficiency—compound over time as systems learn and optimise.
For Australian businesses ready to explore pick and pack automation, the path forward involves assessing current operational pain points, understanding available technologies, and selecting solutions that scale with growth objectives.
SmartlogitecX supports businesses through this evaluation process, helping identify automation strategies tailored to specific operational requirements and industry contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.What are the main types of automated order picking systems?
Systems range from goods-to-person technologies like AS/RS and AMRs that bring items to stationary pickers, to fully robotic solutions handling entire picking and sorting processes autonomously.
2.How does automation improve order accuracy in warehouses?
By minimising human involvement and using barcode scanning, vision systems, and weight verification, automation virtually eliminates common errors including wrong items, incorrect quantities, and mislabelled shipments.
3.Can small businesses benefit from warehouse picking automation?
Yes. Scalable solutions like AMRs, pick-to-light systems, and modular sortation allow smaller operations to automate specific processes without complete facility overhauls. Entry costs have decreased significantly.
4.How do picking robots work in a warehouse environment?
Picking robots combine vision systems to identify products, AI to determine optimal grasping approaches, and robotic arms with specialised grippers to select items and place them into order containers.
5.What is the difference between an AMR and an AGV?
AGVs follow predefined paths using floor-mounted guides. AMRs navigate dynamically using onboard sensors and mapping software, avoiding obstacles and calculating efficient routes in real-time.
6.Does automated picking replace all warehouse workers?
No. Automation typically redefines roles rather than eliminating them. Repetitive and physically demanding tasks shift to machines, whilst employees focus on quality control, exception handling, system maintenance, and oversight functions.
7.What is a Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
A WMS is software, serving as the central control hub for warehouse operations. It manages inventory, directs automated systems, assigns tasks to robots and workers, optimises picking routes, and provides real-time performance data.