Global e-commerce sales are projected to reach $8.1 trillion by 2026, placing unprecedented pressure on supply chains to deliver faster, more accurately, and at lower costs than ever before. For operations managers navigating this landscape, the challenge isn’t simply keeping pace with today’s demands—it’s building a warehouse automation strategy that can evolve alongside business growth without requiring complete system overhauls every few years. This comprehensive guide provides a practical framework for designing a scalable warehouse automation roadmap that balances immediate operational needs with long-term strategic objectives, ensuring your investment in technology delivers sustainable returns whilst maintaining the flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions.
Why a Strategic Roadmap is Crucial for Warehouse Automation Success
The difference between successful warehouse automation and costly technological misadventures often lies not in the sophistication of the equipment chosen, but in the quality of planning that precedes implementation. Without a strategic roadmap, organisations risk investing in warehouse solutions that address symptoms rather than root causes, creating integration nightmares that compound rather than resolve operational inefficiencies. A well-crafted roadmap serves as both a business case for securing stakeholder buy-in and a practical framework for ensuring each technological investment builds upon previous implementations, creating cumulative value rather than isolated improvements. This structured approach to automation transforms what could be a series of reactive purchases into a coherent strategy for operational resilience, where each phase of implementation strengthens the foundation for future growth whilst delivering measurable returns on investment that justify continued advancement toward full automation maturity.
Step 1: Assess Your Current Operations and Define Clear Goals
The foundation of any successful warehouse management transformation begins with a thorough understanding of existing processes, identifying specific bottlenecks where manual handling creates delays, errors accumulate, or safety concerns persist. This operational audit requires mapping the complete material and data flow from receiving through put-away, picking, packing, and shipping, analysing key metrics such as order accuracy rates, dock-to-stock cycle times, labour costs per order, and inventory turnover to establish baseline performance levels. The assessment must go beyond surface-level observations to uncover the root causes of inefficiencies, whether they stem from layout constraints, process design flaws, or technology limitations, enabling the development of SMART objectives that address genuine operational needs rather than perceived problems.
SmartlogitecX recommends focusing this analysis on identifying areas where automation can deliver the most significant impact, whether the primary goal involves increasing throughput capacity, reducing operational costs, improving accuracy rates, or maximising the utilisation of existing warehouse space through more efficient storage configurations.
Step 2: Explore Key Automation Technologies for Modern Warehouses
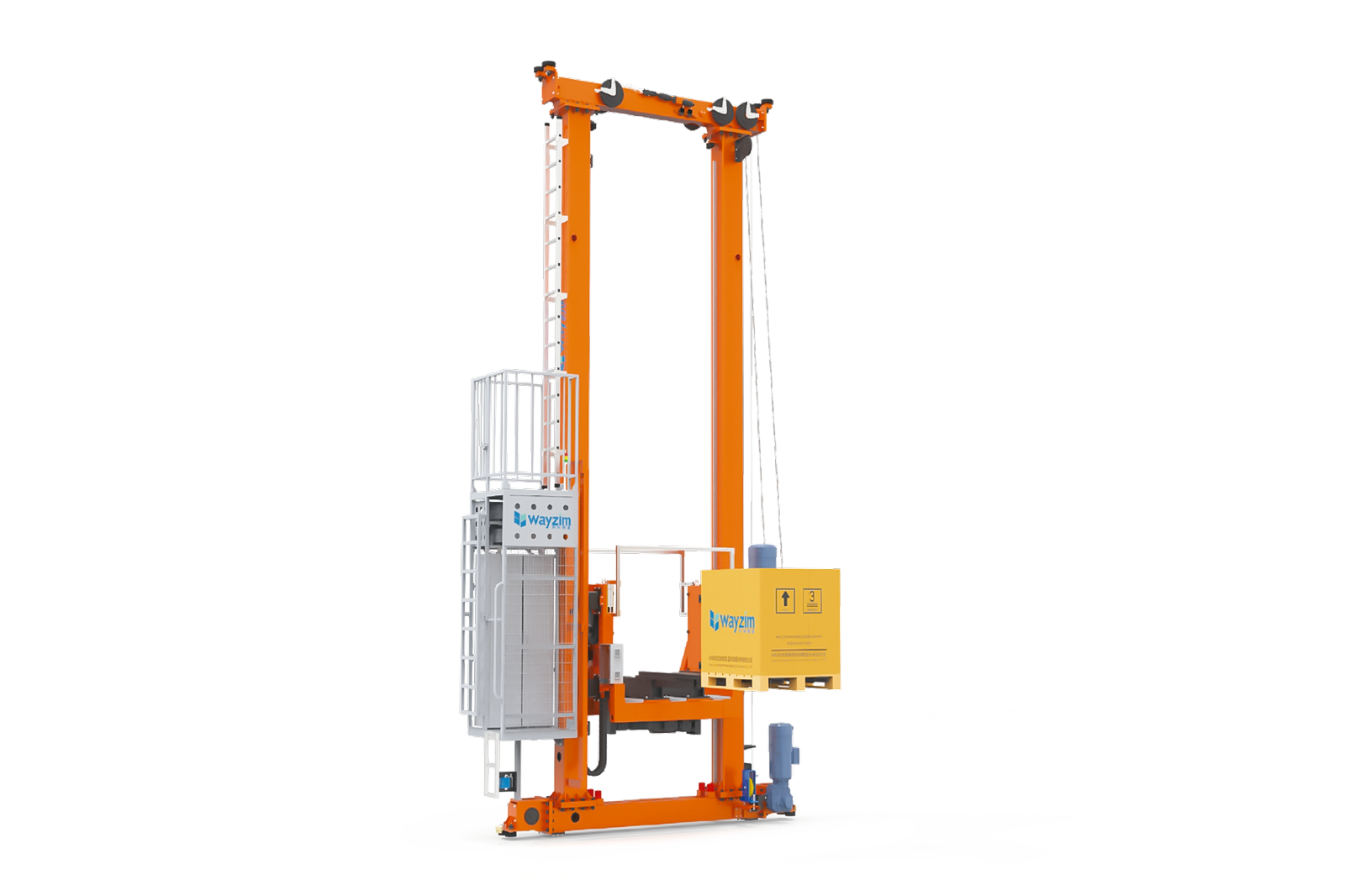
Understanding the landscape of available automated storage and warehouse robotics technologies enables informed decision-making about which solutions best address identified operational challenges. SmartlogitecX Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS) represent one of the most transformative technologies for operations struggling with space constraints or high-volume SKU management, with options ranging from pallet stacker cranes for bulk storage to sophisticated tote-shuttle systems that handle smaller items with remarkable speed and precision.
The evolution of warehouse robotics has introduced Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) that navigate dynamically through facilities using advanced sensors and artificial intelligence, offering greater flexibility than traditional Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) that follow predetermined paths, whilst both technologies dramatically reduce the physical burden on workers and improve picking efficiency. Complementing these mobile solutions, modern warehouse conveyor systems and automated sorting equipment create continuous material flow that minimises manual handling, with belt conveyors, modular designs, and roller systems each offering specific advantages depending on product characteristics and throughput requirements, forming the backbone of any automated warehouse system that seeks to optimise both speed and accuracy across all operational processes.
Step 3: Build Your Phased and Scalable Implementation Plan
Creating a phased approach to introducing advanced material handling technology ensures each stage of automation builds logically upon previous investments whilst minimising operational disruption during transition periods. The prioritisation process should evaluate potential automation projects based on return on investment calculations, operational impact assessments, and strategic alignment with long-term business objectives, typically beginning with high-volume, repetitive processes where automation delivers immediate measurable benefits. A multi-year implementation timeline allows organisations to spread capital expenditure whilst learning from each phase, with Year 1 perhaps focusing on core material handling improvements through conveyor installation, Year 2 introducing automated storage solutions for fast-moving inventory, and Year 3 expanding into robotic picking systems as volumes justify the investment. SmartlogitecX emphasises the importance of selecting modular technologies that accommodate future expansion, such as scalable conveyor systems that extend as needed or AMR fleets that grow incrementally, ensuring new automation components integrate seamlessly with existing Warehouse Management Systems through standardised communication protocols and data exchange formats that prevent the creation of information silos.
Step 4: Measure Success and Calculate Your Return on Investment
Establishing comprehensive performance monitoring systems enables organisations to track the tangible benefits of automation investments whilst identifying opportunities for continuous improvement and future expansion. Essential key performance indicators include throughput increases measured in orders processed per hour, accuracy improvements reflected in reduced error rates and returns, labour cost reductions calculated as cost per unit handled, system uptime percentages that indicate reliability, and inventory accuracy metrics that demonstrate improved stock control. Calculating return on investment requires considering both immediate operational savings from reduced labour requirements and decreased error-related costs, as well as longer-term strategic benefits such as improved workplace safety, enhanced customer satisfaction through faster fulfilment, and increased business agility that enables rapid scaling during demand spikes. SmartlogitecX advocates for using real-time data analytics to monitor these metrics continuously, enabling evidence-based decisions about when to proceed with subsequent automation phases and which areas require additional investment to maximise overall system performance and economic benefits.
Your Next Steps in Warehouse Automation
Moving from strategic planning to practical implementation requires translating the roadmap framework into concrete actions tailored to your specific operational context and business objectives. Begin by conducting the internal assessment outlined in Step 1, engaging cross-functional teams to ensure all perspectives inform the baseline analysis and subsequent automation priorities, then research specific warehouse automation solutions that align with identified needs whilst considering the track record and support capabilities of warehouse automation companies. Evaluate potential warehouse automation products not just on technical specifications but on their compatibility with existing systems, scalability potential, and the vendor’s ability to provide ongoing support and system evolution as your requirements change. SmartlogitecX offers comprehensive consultation services to help organisations navigate this selection process, drawing on extensive experience implementing automated systems across diverse industries to ensure each client’s unique operational challenges receive appropriate technological solutions that deliver sustainable competitive advantages.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.What are the most common challenges in warehouse automation projects?
Integration complexity ranks amongst the primary challenges, as new automated systems must communicate effectively with existing warehouse management software, enterprise resource planning systems, and other operational technologies whilst maintaining data integrity across all platforms.
2.How do I get my team ready for the transition to an automated system?
Successful workforce preparation involves comprehensive training programmes that begin well before system implementation, focusing on building confidence with new technologies whilst emphasising how
automation enhances rather than replaces human expertise in warehouse operations.
3.What is the difference between an AGV and an AMR?
AGVs follow fixed paths using magnetic tape, wires, or other physical guides, offering predictable routing for repetitive tasks, whilst AMRs navigate dynamically using sensors and mapping technology, providing greater flexibility to adapt routes based on obstacles or changing operational requirements.
4.How long does it typically take to see a return on investment from automation?
Most warehouse automation projects achieve positive ROI within 18 to 36 months, though this timeline varies significantly based on implementation scope, operational volumes, and the specific technologies
deployed.
5.Can automation be implemented in an existing warehouse or does it require a new build?
Modern automation solutions accommodate retrofitting into existing facilities through modular designs and flexible configurations, though new construction offers opportunities to optimise layout specifically
for automated operations from the outset.
6.What software is used to manage automated warehouse processes?
Warehouse Control Systems (WCS) coordinate automated equipment operations, whilst Warehouse Execution Systems (WES) optimise workflow orchestration, both integrating with broader Warehouse Management Systems to ensure cohesive operational control.
7.How does automation improve workplace safety?
Automation reduces manual handling of heavy items, minimises forklift traffic in pedestrian areas, and eliminates repetitive strain injuries associated with picking and packing operations, creating safer working environments for remaining human workers.
8.What are the first steps to plan for a new material handling system?
Initial planning involves documenting current material flows, analysing throughput requirements, identifying constraint points, and establishing clear performance objectives that guide subsequent technology selection and implementation planning.
9.How do you make an automated logistics solution scalable for future growth?
Scalability requires selecting modular technologies with expansion capabilities, implementing robust data architecture that accommodates increased transaction volumes, and designing physical layouts that allow for equipment additions without major infrastructure modifications.
10.What are the main benefits of automating storage and retrieval operations?
Automated storage maximises vertical space utilisation, improves inventory accuracy through systematic tracking, reduces product damage from handling errors, and enables 24/7 operations that significantly
increase facility throughput capacity.