Introduction
With e-commerce demand pushing fulfilment centres to capacity, Australian businesses are turning to warehouse automation to remain competitive. Customer expectations for next-day delivery continue to rise, labour shortages persist across the logistics sector, and operational efficiency has become non-negotiable for sustainable growth.
These pressures have accelerated the adoption of warehouse automation solutions that streamline operations, reduce errors, and scale with demand. SmartlogitecX works with Australian businesses navigating this transformation, helping them identify and implement technologies suited to their specific operational requirements.
This guide explores the top 10 warehouse automation technologies reshaping logistics and supply chains in 2025, from foundational storage systems to emerging innovations that are redefining what modern warehousing looks like.
1. Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS)
What ASRS technology delivers
SMartlogitecX Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems are computer-controlled solutions that automatically store and retrieve goods from defined locations within a facility. These systems represent one of the most significant opportunities for warehouses seeking to maximise their existing footprint.
The benefits are substantial. ASRS technology can recover up to 85% of floor space compared to traditional shelving, dramatically increasing storage density. Beyond space utilisation, these systems improve inventory control accuracy and enhance picking precision—critical factors for high-volume operations where errors carry significant costs.
Types of ASRS solutions
Several ASRS configurations serve different operational requirements. SmartlogitecX Vertical Lift Modules (VLMs) work well for facilities with limited floor space but available height. Shuttle systems excel in high-throughput environments requiring rapid retrieval. Carousel systems suit operations with smaller items and moderate volume demands.
Understanding which configuration aligns with your throughput requirements, SKU profile, and facility constraints determines whether an ASRS investment delivers expected returns.
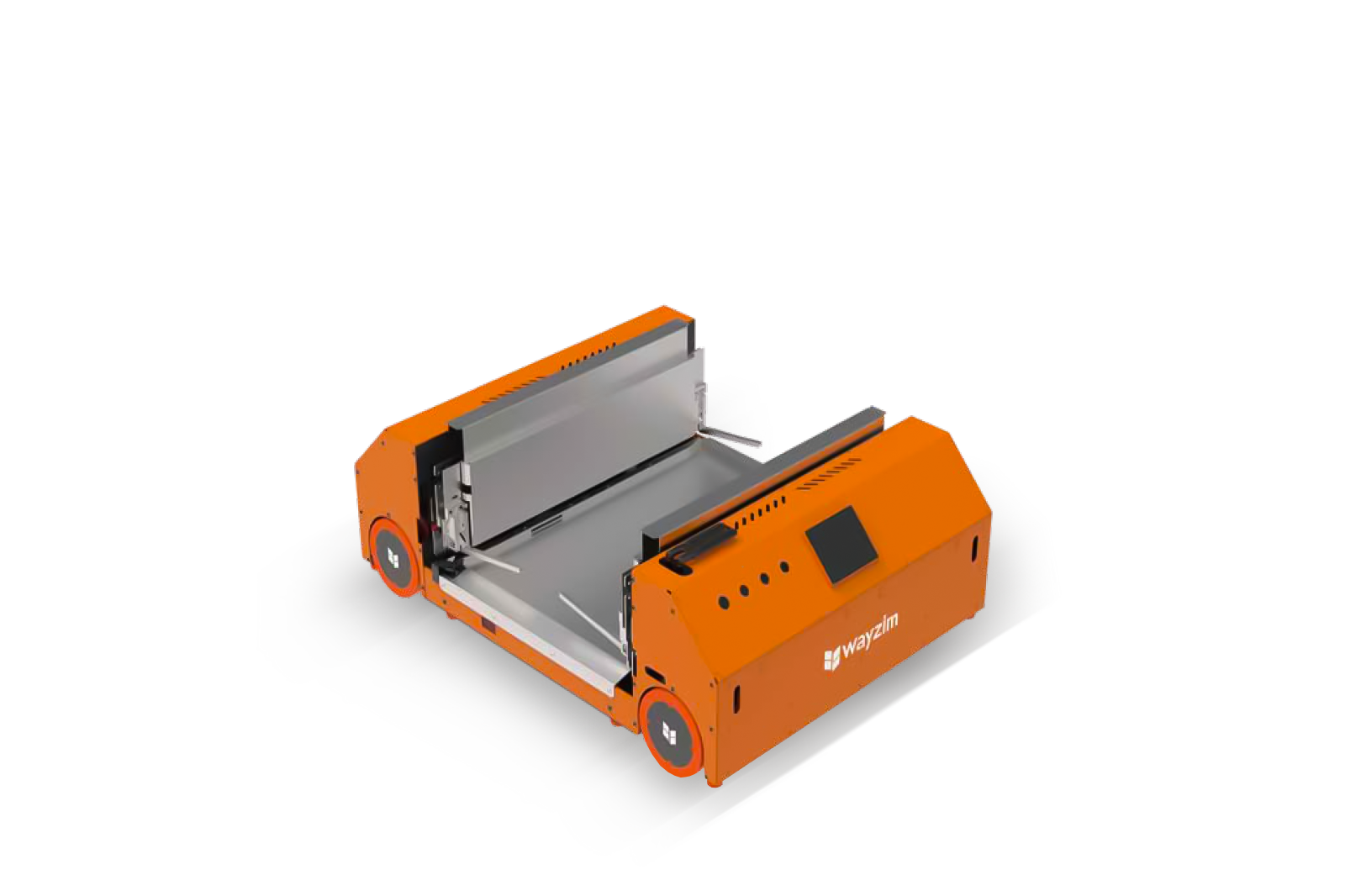
2. Advanced Warehouse Robotics
Robotics has evolved beyond simple repetitive tasks to become an intelligent, adaptive component of the warehouse ecosystem. Modern warehouse robotics solutions handle complex operations while working alongside human teams.
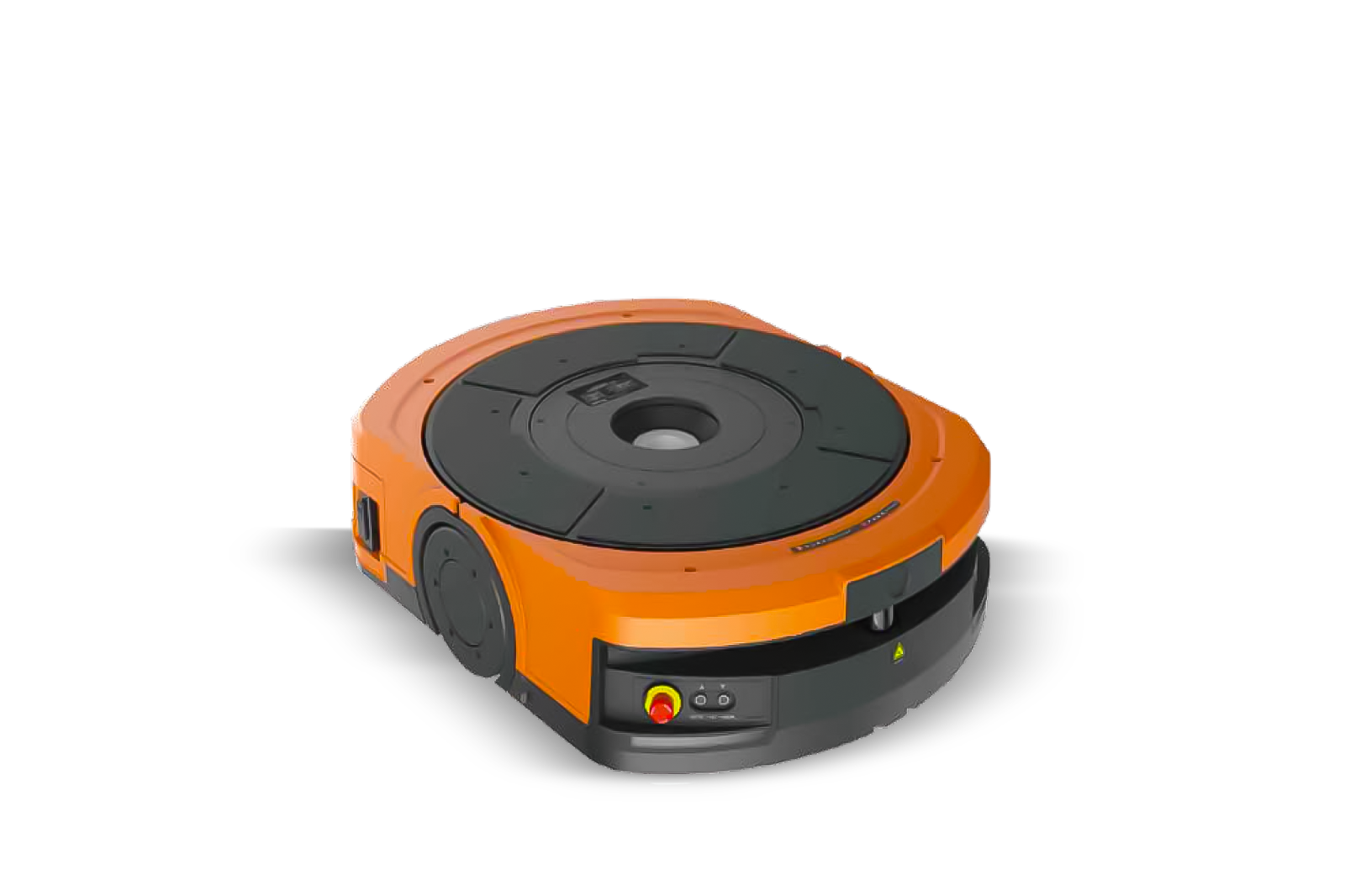
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) and AGVs
Two primary categories of mobile robots serve different operational needs. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) follow fixed paths—typically magnetic strips or painted lines on the floor—making them reliable for consistent, high-volume routes. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) use sensors and AI to navigate dynamically, creating their own routes and avoiding obstacles in real time.
Both technologies reduce manual travel time significantly. In goods-to-person workflows, these robots transport inventory directly to stationary picking stations, eliminating the need for workers to traverse warehouse aisles repeatedly.
Robotic picking arms and collaborative robots
Robotic arms powered by AI and machine vision now pick and place individual items with speed and accuracy that matches or exceeds human performance for certain tasks. These systems excel with uniform products and predictable handling requirements.
Collaborative robots—cobots—work safely alongside human employees on tasks like packing, sorting, and quality inspection. Rather than replacing workers, cobots handle physically demanding or repetitive elements while humans focus on exception handling and complex decision-making.
3. Intelligent Software and AI-Driven Optimisation
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
A Warehouse Management System serves as the software brain directing all warehouse operations. Modern WMS platforms integrate with automation technologies like ASRS and robotics, orchestrating workflows across the entire facility.
Key capabilities include real-time inventory tracking, order management, labour planning, and performance analytics. SmartlogitecX partners with leading WMS providers to deliver integrated warehouse automation solutions that give Australian operations end-to-end visibility and control.
Without robust WMS integration, even the most advanced physical automation operates below its potential. The software layer determines how effectively hardware investments translate into operational improvements.
AI and machine learning for predictive logistics
Artificial intelligence and machine learning analyse operational data to optimise processes continuously. Practical applications include demand forecasting that optimises inventory levels before seasonal peaks, route optimisation calculating efficient picking paths for robots and humans, and predictive maintenance identifying potential equipment failures before they cause downtime.
AI functions as the enabling technology making all other automation smarter and more responsive to changing conditions.
4. Conveyor, Sortation, and IoT Connectivity
High-speed conveyor and sortation systems
Modern warehouse conveyor and sortation systems have advanced considerably beyond traditional roller conveyors. High-speed sorters—including cross-belt and pop-wheel configurations—rapidly move and sort cartons, totes, and individual items to specific destinations throughout a facility.
For high-volume e-commerce fulfilment centres processing thousands of orders daily, automated sortation is essential for meeting throughput requirements without proportional increases in labour costs.
IoT for real-time visibility
The Internet of Things creates a network of sensors, RFID tags, and smart devices collecting and sharing data across warehouse operations. This connectivity enables real-time asset tracking showing exact inventory and equipment locations, environmental monitoring for temperature-sensitive goods, and equipment health data feeding predictive maintenance systems.
IoT provides the visibility foundation that makes truly optimised operations possible.
5. Human-Augmentation and Emerging Technologies
Voice and vision picking technologies
Voice picking equips operators with headsets delivering verbal instructions—enabling hands-free, eyes-up operation that improves both safety and productivity. Vision picking using smart glasses overlays digital information onto a worker’s field of view, displaying pick locations and quantities without requiring workers to consult handheld devices.
These technologies enhance human performance within automated environments, representing effective human-robot collaboration rather than replacement.
Drones for inventory management
Autonomous drones equipped with scanners perform cycle counting and inventory audits faster than manual methods, particularly in facilities with high racking systems. Drone-based counting proceeds without disrupting normal operations, improving inventory accuracy while reducing the labour hours traditionally required for stock verification.
SmartlogitecX monitors emerging technologies to help clients future-proof their automation investments as these solutions mature.
The Path Forward for Automated Warehouses
Warehouse automation has shifted from competitive advantage to operational necessity for businesses building resilient, efficient supply chains. The technologies covered here—from ASRS and robotics to AI-driven software and IoT connectivity—work together to create facilities that respond intelligently to changing demands.
The objective is not replacing human workers but augmenting their capabilities, creating safer environments where people focus on high-value tasks while automation handles repetitive, physically demanding work.
For Australian businesses evaluating their automation roadmap, SmartlogitecX offers tailored assessments matching technology solutions to specific operational requirements and growth objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.How does warehouse automation transform the supply chain?
Automation increases processing speed, improves order accuracy, reduces operational costs, and provides resilience to handle demand fluctuations and disruptions.
2.What are the main benefits for order fulfilment?
Faster processing times, higher order accuracy, reduced labour costs, and real-time inventory visibility leading to improved customer satisfaction.
3.What challenges should businesses expect during implementation?
High initial investment, integration complexity with existing systems, employee training requirements, and potential operational disruption during rollout.
4.Will warehouse robots replace human workers?
The trend favors collaboration. Robots handle strenuous, repetitive tasks while humans focus on complex roles like quality control and exception handling.
5.What distinguishes an AGV from an AMR?
AGVs follow fixed paths using floor markings. AMRs navigate dynamically using sensors and AI, creating routes and avoiding obstacles independently.
6.Can small and medium businesses afford automation?
Yes. Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS) models and modular solutions allow smaller operations to adopt automation with lower upfront investment.